Asset Disposal: Benefits and Examples

An asset’s salvage value subtracted from its basis (initial) cost determines the amount to be depreciated. Most businesses utilize the IRS’s Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) or Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) methods for this process. The truck’s book value is $7,000, but nothing is received for it if it is discarded. The most common ways to evaluate asset’s disposal are through net book value and carrying value.
What Is an Asset’s Salvage Value?
Theoretically, this provides a more accurate estimate of the true expenses of maintaining the company’s operations each year. Depreciation is an accounting technique that lets companies allocate the initial cost of an asset to each year of its useful life. This helps them match their expenses and revenues more accurately and calculate taxable income for a specific period. Yes, salvage value can be considered the selling price that a company can expect to receive for an asset the end of its life.
Journal Entries of Asset Disposal with Losses
A trading disposal is done when the company intends to buy and use an asset as soon as they’ve received it. It is a type of normal disposal that just involves goods instead of cash. For disposal value example, if you own a retail store then you may be trading in old goods you no longer want. You would do this in exchange for a store credit to buy new goods for your shelves instead.
Asset Impairment and Disposal
Additionally, consider the example of a business owner whose desk has a useful life of seven years. How much the desk is worth at the end of seven years (its fair market value as determined by agreement or appraisal) is its residual value, also known as salvage value. This information is helpful to management to know how much cash flow it may receive if it were to sell the desk at the end of its useful life. Residual value formulas differ across industries, but its general meaning—what remains—is constant.
- The residual value of a car is calculated by the bank or financial institution; it is typically calculated as a percentage of the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP).
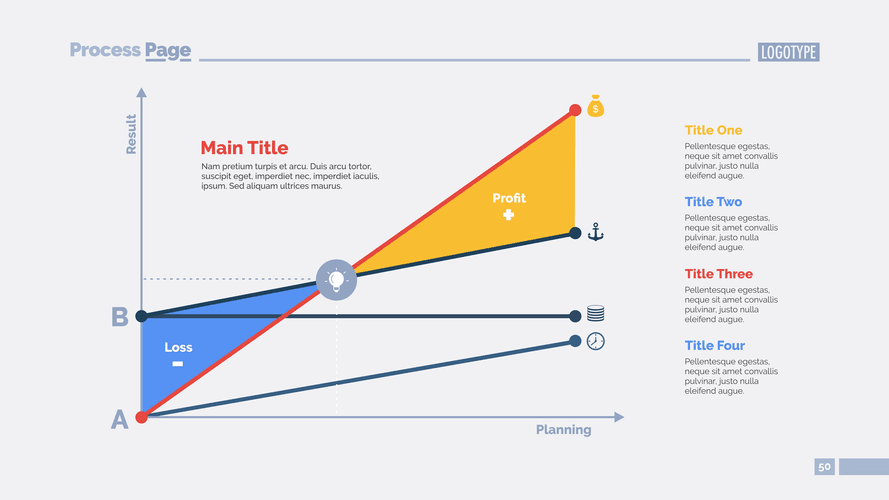
- The company breaks even on the disposal of a fixed asset if the cash or trade-in allowance received is equal to the book value.
- In other contexts, residual value is the value of the asset at the end of its life less costs to dispose of the asset.
- Hazardous waste transporters play an important role in this system, delivering waste from the point of generation to an ultimate destination.
- This amount is carried on a company’s financial statement under noncurrent assets.
As a result of this journal entry, both account balances related to the discarded truck are now zero. When a fixed asset that does not have a residual value is fully depreciated, its cost equals its Accumulated Depreciation balance and its book value is zero. A company may no longer need a fixed asset that it owns, or an asset may have become obsolete or inefficient.

- Finally, keep an eye out for better alternatives that might be available instead of holding on to assets you don’t need.
- For other assets, companies aim to have a residual value as high as possible.
- An asset’s salvage value subtracted from its basis (initial) cost determines the amount to be depreciated.
- 2) Understanding your legal obligations when it comes to disposing of assets.
- The truck’s book value is $7,000, but nothing is received for it if it is discarded.
- Even if the company receives a small amount, it may be offset by costs of removing and disposing of the asset.
- For example, a machine has been installed in a factory and after a useful working on its life period needs to be replaced with a new model.
A strong example is assets that must adhere to regulatory disposal requirements to remove waste without environmental contamination. Discover how to identify your depreciable assets, calculate their salvage value, choose the most appropriate salvage value accounting method, and handle salvage value changes. Depreciation needs to be taken into account when recording the disposal of a non-current asset. A company may dispose of a fixed asset by trading it in for a similar asset. The company receives a trade-in allowance for the old asset that may be applied toward the purchase of the new asset.
Resources for Your Growing Business

Gains are increases in the business’s wealth resulting from peripheral activities unrelated to its main operations. Recall that revenue is earnings a business generates by selling products and/or services to customers in the course of normal business operations. That is, earnings result from the business doing what it was set up to do operationally, such as a dry cleaning business cleaning customers’ clothes.
Conservative accounting practices dictate that when in doubt, it is more prudent to use a faster depreciation schedule so that expenses are recognized earlier. In that way, if the asset does not live out the expected life, the company does not incur an unexpected accounting loss. A fully depreciated asset is a property, plant or piece of equipment (PP&E) which, for accounting purposes, is worth only its salvage value. Whenever an asset is capitalized, its cost is depreciated over several years according to a depreciation schedule.



 المنصة التعليمية
المنصة التعليمية دولة اﻹمارات
دولة اﻹمارات اقتصاد
اقتصاد تسوق
تسوق ثقافة وعلم
ثقافة وعلم ترفيه وفن
ترفيه وفن عن شبكة مقروء
عن شبكة مقروء